Future of Food: 4 US Agricultural Innovations to Watch in the Next 18 Months

The Future of Food: 4 US Agricultural Innovations to Watch in the Next 18 Months is rapidly taking shape as groundbreaking technologies emerge from research labs and pilot programs into mainstream adoption. These advancements promise to reshape how food is grown, processed, and distributed, addressing critical challenges like sustainability, resource efficiency, and food security.
Precision Agriculture and AI Integration
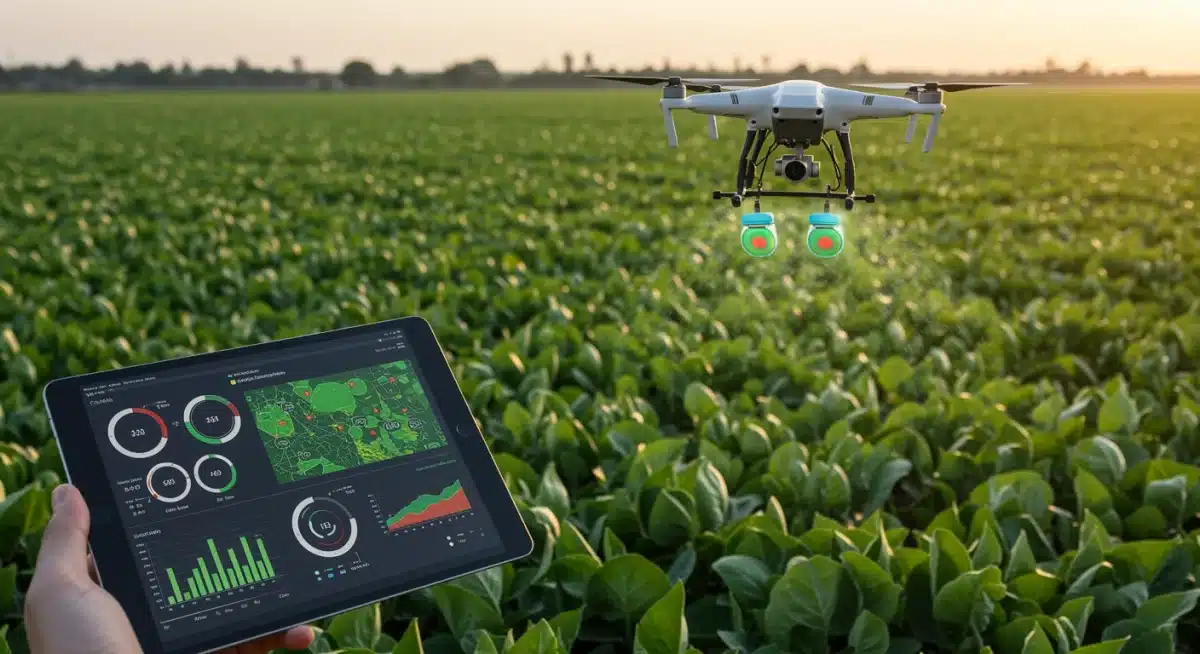
Precision agriculture, powered by artificial intelligence (AI), is transforming how farmers manage their fields. This technology allows for highly localized and optimized application of resources, moving beyond broad-stroke farming methods to a more granular approach. The focus is on maximizing yield while minimizing environmental impact.
Real-time Data and Predictive Analytics
Farmers are increasingly adopting AI-driven platforms that gather real-time data from various sources, including sensors, drones, and satellite imagery. This data provides crucial insights into soil health, crop growth, moisture levels, and pest infestations. Predictive analytics then utilize this information to forecast potential issues and recommend precise interventions.
- Optimized Resource Use: AI algorithms can determine the exact amount of water, fertilizer, and pesticides needed for specific areas, reducing waste and runoff.
- Early Disease Detection: Machine learning models analyze visual data to identify early signs of plant diseases or pest outbreaks, allowing for timely and targeted treatment.
- Yield Forecasting: Advanced analytics provide accurate yield predictions, helping farmers plan harvesting, storage, and market distribution more effectively.
The integration of AI makes farming not just more efficient but also significantly more sustainable. By reducing chemical inputs and water usage, it lessens the ecological footprint of agricultural operations across the US.
Vertical Farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Vertical farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) are rapidly expanding, offering solutions to land scarcity and climate variability. These indoor farming methods allow for year-round production in urban areas, closer to consumers, drastically cutting transportation costs and emissions.
Technological Advancements in CEA
Recent breakthroughs in LED lighting, hydroponics, and aeroponics are making vertical farms more energy-efficient and productive. These systems create optimal growing conditions, independent of external weather patterns, ensuring consistent quality and yield.
- LED Spectrum Optimization: New LED technologies allow growers to fine-tune light spectrums to specific crop needs, accelerating growth and enhancing nutritional content.
- Automated Nutrient Delivery: Hydroponic and aeroponic systems now feature highly automated nutrient delivery, ensuring plants receive precise amounts of water and minerals.
- Robotics for Labor Reduction: Robots are being deployed for tasks such as planting, harvesting, and monitoring, reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency in these controlled environments.
As of late 2023, several major vertical farming companies in the US have secured significant funding, indicating strong investor confidence and a clear path to scaling operations within the next 18 months. This expansion is poised to bring fresh, locally grown produce to more communities nationwide.

Biotechnology and Gene Editing for Crop Improvement
Biotechnology, particularly advanced gene-editing techniques like CRISPR, is revolutionizing crop improvement. These innovations allow scientists to precisely modify plant genomes to enhance desirable traits, making crops more resilient, nutritious, and productive.
CRISPR and Drought-Resistant Crops
CRISPR technology enables targeted changes to DNA, facilitating the development of crops with enhanced resistance to diseases, pests, and environmental stressors like drought and extreme temperatures. This is crucial for maintaining food security in the face of climate change.
Current research, as reported by institutions like the USDA and leading agricultural universities, indicates that several gene-edited crop varieties are nearing commercialization. These include drought-tolerant corn and soybeans, and disease-resistant tomatoes, expected to hit markets or be widely tested within the next 18 months.
The precision of gene editing offers a significant advantage over traditional breeding methods, allowing for faster development of improved varieties without introducing foreign DNA. This leads to crops that are not only more robust but also perceived as safer by regulators and consumers.
Alternative Protein Production
The demand for sustainable protein sources is driving rapid innovation in alternative protein production. This category includes plant-based proteins, cultivated meat (also known as cell-based or lab-grown meat), and insect-based proteins. These alternatives aim to reduce the environmental impact associated with traditional livestock farming.
Cultivated Meat Scaling Up
Cultivated meat companies in the US are making significant strides in scaling production. Following recent regulatory approvals, several firms are actively working to increase manufacturing capacity and reduce costs, bringing these products closer to widespread consumer availability.
- Regulatory Progress: The FDA and USDA have established regulatory pathways for cultivated meat, paving the way for market entry.
- Production Efficiency: New bioreactor designs and cell culture media formulations are improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of cultivated meat production.
- Consumer Acceptance: Ongoing efforts in consumer education and product development are addressing concerns and improving the sensory experience of alternative proteins.
Within the next 18 months, consumers can anticipate a greater variety of cultivated meat products becoming available in select markets, as well as a continued expansion of plant-based options in both retail and foodservice sectors. This shift represents a fundamental change in how protein is sourced and consumed.
Water Management and Conservation Technologies
Effective water management is paramount for the future of US agriculture, especially in regions facing increasing water scarcity. Innovations in irrigation systems, water recycling, and atmospheric water generation are providing crucial solutions to optimize water use and minimize waste.
Smart Irrigation Systems and Sensors
Smart irrigation systems are gaining traction, utilizing sensors and real-time data to deliver water precisely when and where it’s needed. These systems can adapt to weather conditions, soil moisture levels, and crop-specific requirements, significantly reducing water consumption compared to traditional methods.
- Sensor Networks: In-field sensors continuously monitor soil moisture and plant stress, providing data to optimize irrigation schedules.
- Automated Drip Systems: Advanced drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
- Weather Integration: Systems integrate with hyper-local weather forecasts to adjust watering plans, preventing over-irrigation during rainy periods.
Beyond irrigation, research into water recycling and purification technologies for agricultural runoff is progressing, aiming to create closed-loop systems that reuse water multiple times. Atmospheric water generators, while still niche, are also being explored for niche applications in arid regions, demonstrating a holistic approach to water conservation.
Sustainable Packaging and Supply Chain Optimization
The agricultural sector is also seeing significant innovation in sustainable packaging and supply chain optimization. These advancements aim to reduce food waste, minimize environmental impact, and improve the efficiency of getting food from farm to table.
Biodegradable and Compostable Packaging
New materials are emerging that offer viable alternatives to traditional plastic packaging. These include plant-based plastics, mushroom-based packaging, and other biodegradable or compostable options designed to break down harmlessly after use. This directly addresses the growing concern over plastic pollution in the food industry.
As reported by industry analysts and sustainable packaging consortiums, the adoption of these materials is expected to accelerate in the next 18 months, driven by consumer demand and corporate sustainability goals. Food producers are investing in research and development to ensure these new packaging solutions maintain product integrity and shelf life.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology is being piloted to enhance transparency and traceability within agricultural supply chains. This allows for real-time tracking of produce from farm to consumer, improving food safety, reducing fraud, and enabling more efficient recall processes if needed.
- Enhanced Traceability: Consumers can scan QR codes to access detailed information about a product’s origin, journey, and certifications.
- Reduced Food Waste: Better visibility in the supply chain helps identify inefficiencies and potential spoilage points, allowing for quicker intervention.
- Improved Food Safety: Rapid identification of affected batches in case of contamination minimizes public health risks and economic losses.
These innovations in packaging and supply chain management are crucial for building a more resilient and environmentally responsible food system, contributing to a holistic approach to agricultural sustainability.
| Key Innovation | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture & AI | Optimizing resource use and yield through data-driven insights and predictive analytics. |
| Vertical Farming (CEA) | Year-round indoor crop production, reducing land use and transportation needs. |
| Biotechnology & Gene Editing | Developing resilient, nutritious crops with enhanced traits using advanced genetic modification. |
| Alternative Proteins | Scaling production of plant-based and cultivated meats to meet sustainable protein demand. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Agricultural Innovations
Precision agriculture uses technology like AI, sensors, and drones to monitor and optimize crop conditions on a micro-level. This allows farmers to apply resources like water and fertilizer precisely where needed, reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
Vertical farming enables food production in urban areas, closer to consumers. This reduces transportation costs and carbon emissions, making fresh produce more accessible year-round and less susceptible to external climate conditions.
Gene-edited crops, particularly those developed with CRISPR technology, involve precise modifications to a plant’s existing DNA. Regulatory bodies like the USDA and FDA assess their safety, often finding them comparable to conventionally bred crops, with no foreign DNA introduced.
Alternative proteins, such as plant-based and cultivated meats, offer significant environmental benefits. They typically require less land, water, and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional animal agriculture, contributing to a more sustainable food system.
AI analyzes vast amounts of agricultural data to provide insights for decision-making. It powers predictive analytics for yield forecasting, automates irrigation systems, detects diseases early, and optimizes resource allocation, making farming more efficient and data-driven.
Looking Ahead
The convergence of these US agricultural innovations signals a pivotal moment for global food systems. Within the next 18 months, we can expect to see increased commercialization and broader adoption of these technologies, especially in precision agriculture and alternative proteins. The ongoing challenges of climate change and food security will continue to drive investment and research, pushing these innovations from niche applications to mainstream solutions. Stakeholders across the food chain, from farmers to consumers, will feel the profound impact of these transformative shifts.